(a) the main performance parameters of the pump
Pump performance parameters are mainly flow and head, in addition to shaft power, efficiency, speed and the necessary cavitation margin.
- Flow rate refers to the amount of liquid output per unit time through the pump outlet, generally using volume flow or mass flow. The volume of liquid actually transported by the pump per unit time is called the pump flow rate.It's usually denoted by the letter Q. The unit is m/h and L/s.The flow of the pump, that is, the amount of water, generally should not be selected too large, otherwise, increase the cost of buying the pump; Large flow, large power, but also increase the cost of line, electrical control. It should be analyzed on a case-by-case basis.
- Head refers to the increase in energy per unit weight of the liquid flowing through the pump, that is, the difference between the pressure of the liquid at the pump outlet and the inlet, usually represented by the letter H. The unit is m. Standard use: Pa, HPA, KPa, MPa. In addition: MMHG, KGF /cm. The so-called head is the total head required, not the lifting height, which is particularly important in choosing a pump. Pump head is about 1.15 ~ 1.20 times of water lifting height. For example: the vertical height of a water source to water is 20 meters, and the required head is about 23 ~ 24 meters. When choosing the pump, the head on the pump sample (nameplate) should be close to the required head. In this case, the efficiency of the pump is the highest and the use will be more economical. But it is not necessarily required to be absolutely equal, "as long as the deviation is not more than 20%, the pump can work in the case of more energy saving.
- Inlet pressure Ps and outlet pressure Pd, inlet and outlet pressure refers to the pressure at the flange of the inlet and outlet pipe of the pump, the size of the inlet and outlet pressure affects the pressure resistance of the shell and the requirements of the shaft seal.
- temperature T refers to the pump inlet medium temperature, generally should be given in the process of pump inlet medium normal, minimum and maximum temperature.
- Device NPSHa, also known as effective NPSH.
- Operation state: continuous operation and intermittent operation.
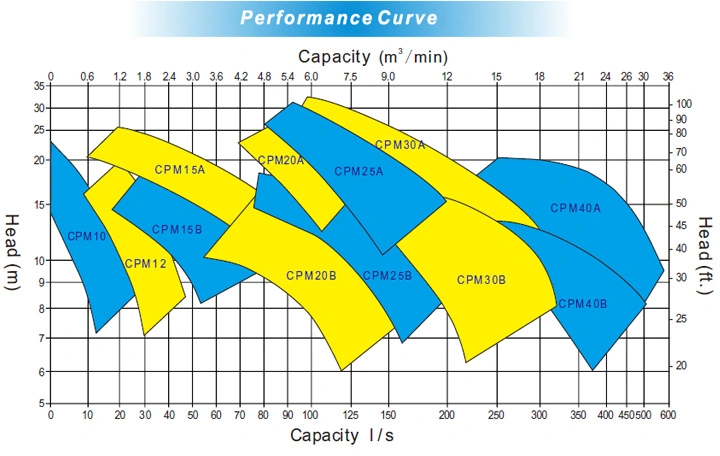
- Performance curve of pumpUsually the relationship between the main performance parameters of the curve is called the pump performance curve or characteristic curve, in essence, the pump performance curve is the liquid in the pump of the external expression of the law of movement, obtained through measurement. Characteristic curves include: Flow (Q - H) - the head curve, traffic - efficiency curve (Q - eta), flow rate (Q - N) - power curve, traffic - NPSH curve - (NPSH) r (Q), the flow of the pump performance curve arbitrarily, can find a set of the curve and its relative lift, power, efficiency and cavitation surplus value, This group of parameters is called the working state, referred to as the working condition or working point, the working condition of the highest efficiency point of the centrifugal pump is called the best working point, and the best working point is generally the design working point.

(b) the physical and chemical properties of the conveying medium
The physical and chemical properties of the conveying medium directly affect the performance, material and structure of the pump, which is an important factor to be considered when selecting the pump. The physical and chemical properties of the medium include: medium name, medium characteristics (such as corrosion, corrosion resistance, toxicity, etc.), solid particle content and particle size, specific gravity, density, viscosity, vaporization pressure, etc. If necessary, the gas content in the medium should also be listed, indicating whether the medium is easy to crystallize.
(c) Site conditions
- Site conditions include the installation position of the pump (indoor and outdoor), environmental temperature, relative humidity, atmospheric pressure, atmospheric corrosion status and classification conditions of dangerous areas. Danger zones include: flammable, explosive, toxic, high temperature, high altitude and other special occasions.
- other factors: the selection of site conditions should be considered, the cost of the project, installation height, etc., so as to decide what kind of structure of the pump type, such as horizontal pump, vertical pump, liquid pump, self-priming pump, etc.
