Due to the depths in which boreholes are drilled, the holes are typically narrow (just over 4”) with the pumps sold according to borehole size as well as capacity and pressure. Borehole pumps are typically longer than standard pumps of equivalent capacities as they are extended to make up for the narrow space in which they may be installed.
Borehole motors are typically filled with water or oil (non-toxic) cooled for bearing lubrication with sealing via a mechanical seal. The cable leaves the motor via a cable gland.
The cable is manufactured according to the depth of the borehole. As cables lengthen there is an associated voltage drop, meaning once cables reach set lengths, the cable diameter must be increased in order to deliver sufficient power to the motor.
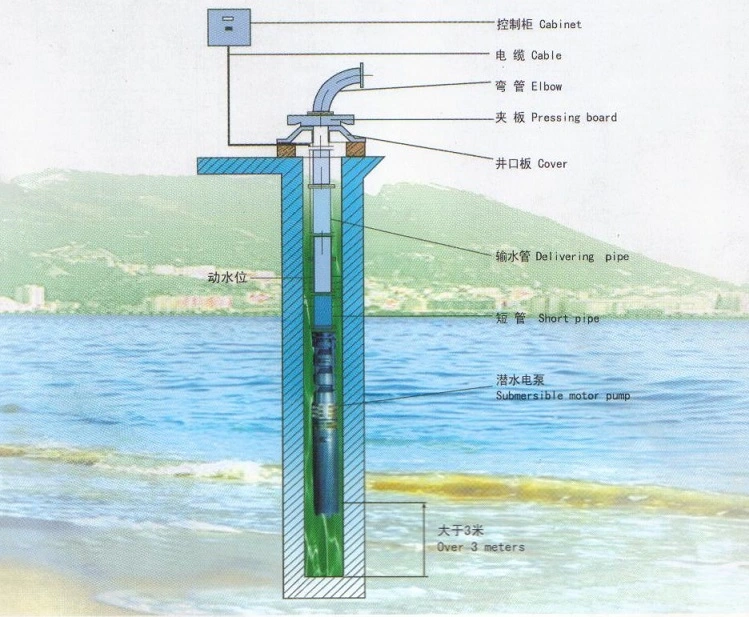
How does a Borehole pumps (deep well pumps) Work?
Units work by a motor driving a shaft which in turn drives either one or several impellers. The motor is at the bottom of the pump, with the pump located above the motor. The pump intake is in the middle of the unit, with the discharge at the top contrary to all other pump designs.
The first impeller draws fluid through a suction strainer, where fluid passes through to the diffuser. If the unit is of single impeller design liquid then passes around the non-return valve exiting the pump. Should the design be of multi impeller construction liquid repeatedly enters a suction casing, then discharge casing across several impellers, before passing around the non-return valve and exiting the pump. Impellers are usually of the closed or semi-open axial design if handling sand.
Designs
Designs of pumps can be single-stage or multistage impeller designs. Some single-stage designs such as our PR Range provide high flows at medium heads (up to 160M). The single impeller design is in technopolymer meaning it floats, allowing the pump to handle 300g/m³ of sand where water is abstracted from bodies of water containing high sand content. Normally units can only accommodate up to 50g/m³ of sand.
Multistage designs are unable to accommodate such high amounts of sand and are used for delivering lower flows at high pressure unless equipped with a floating impeller design.
Construction can be of cast or pressed metal. The Cast design does not have welds that can be attacked by seawater, ensures parts are thicker, improving Borehole Pump Exploded Viewdurability and accommodating of small particles which would ordinarily damage pressed pumps.
Motors can be wound to be operated Direct Current (DC) for power via Solar, or 3 phase motors. It is usually better to have borehole motors generated by three-phase electricity in remote locations & communities as they are far easier to maintain with limited expertise and tools. DC motors can be difficult to maintain due to their design, and expertise can be sometimes lacking.
Cooling Shroud / Sleeve
Borehole pumps can be mounted vertically and horizontally. When installed horizontally or in an open body of water a cooling sleeve is required to ensure the motor is cooled when fluid velocity is below the minimum required.
The unit ensures water velocity is increased past the motor providing the required cooling preventing motor overheating.
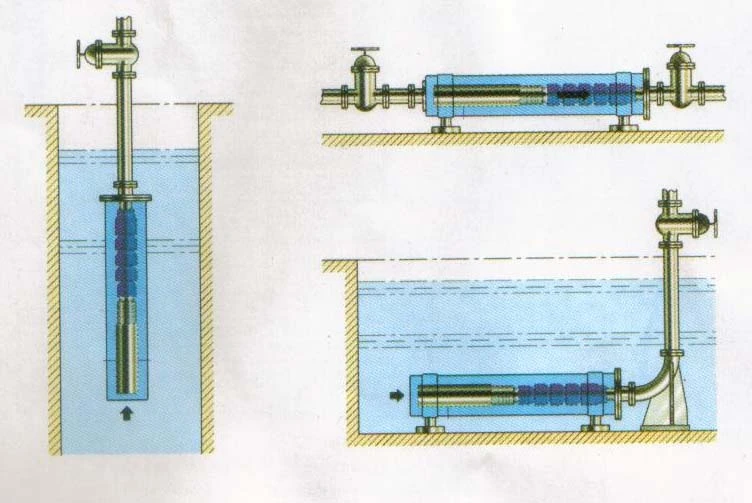
Typical applications for borehole pumps include drainage, irrigation, drinking water supply, lowering of groundwater in mines, and excavations in buildings. They are also used to supply seawater to oil rigs, in which the vertical distance can be over 50M from the pump to the platform.
View our range of Borehole Pumps (deep well pumps)
